Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Clinic
IBD & IBS Clinics
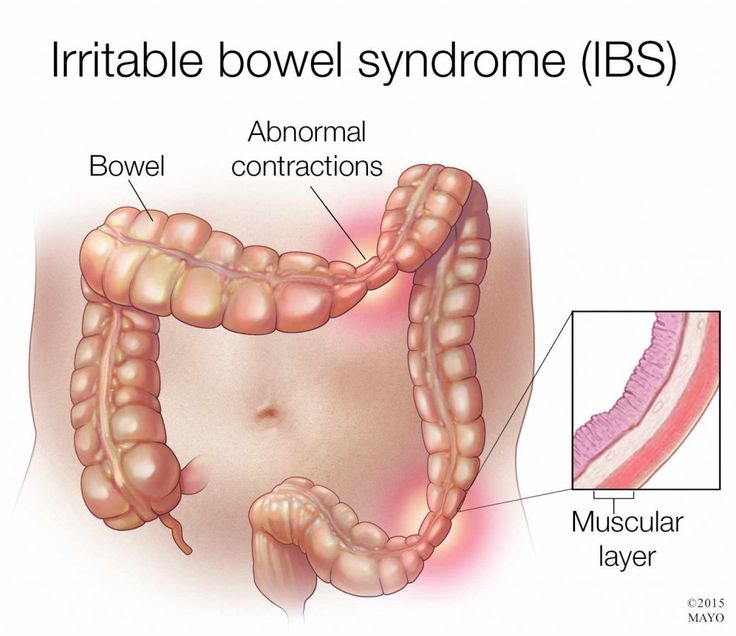
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common functional gastrointestinal disorder that affects the large intestine. It is characterized by a group of symptoms, including abdominal pain, bloating, cramping, and changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea (IBS-D), constipation (IBS-C), or a combination of both (IBS-M). Unlike other digestive conditions, IBS does not cause structural damage or increase the risk of more severe diseases, such as cancer, but it can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
The exact cause of IBS is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of factors, including abnormal gut-brain communication, heightened intestinal sensitivity, changes in gut motility, and imbalances in the gut microbiome. Stress, certain foods, and hormonal changes often act as triggers, exacerbating symptoms.
Diagnosis of IBS is typically based on symptom patterns and criteria, such as the Rome IV criteria, after ruling out other conditions like celiac disease or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Tests may include blood work, stool tests, or imaging studies.
Treatment focuses on symptom management and involves a multifaceted approach. Dietary modifications, such as following a low-FODMAP diet, are often effective in reducing symptoms. Over-the-counter medications may help manage diarrhea or constipation, while antispasmodics and probiotics are used for pain and gut health. In some cases, psychological therapies like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) or medications targeting the gut-brain axis, such as antidepressants, are beneficial.
IBS is a chronic condition with no cure, but symptoms can be controlled with appropriate lifestyle changes, stress management, and treatment. Awareness and understanding of IBS are critical for reducing its social stigma, enabling patients to seek timely care, and improving their overall quality of life.
Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain or cramping, often relieved by bowel movements.
- Bloating and gas.
- Changes in bowel habits (diarrhea, constipation, or alternating between the two).
- Urgency to have a bowel movement.
- Mucus in the stool.
The exact cause of IBS is unknown, but several factors may contribute, including:
- Abnormal muscle contractions in the intestine.
- Hypersensitivity of the gut.
- Gut microbiota imbalances.
- Stress and psychological factors.
- Food sensitivities.
- Post-infectious IBS.
Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Options include:
- Dietary changes (e.g., low-FODMAP diet, increased fiber).
- Stress management techniques (e.g., relaxation, yoga, therapy).
- Medications (e.g., antispasmodics, antidiarrheals, laxatives, antidepressants).
- Probiotics.
Stress can exacerbate IBS symptoms. The gut and brain are closely connected, and stress can affect gut motility and sensitivity.
You should see a doctor if you experience:
- Persistent abdominal pain.
- Changes in bowel habits.
- Rectal bleeding.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Symptoms that interfere with your daily life.