Endoscopic Ultrasound(EUS)
Endoscopic Ultrasound(EUS)
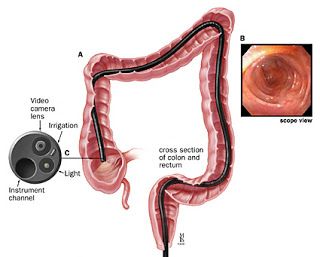
An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a medical procedure that allows your doctor to obtain detailed images and information about your digestive tract and surrounding organs. During an EUS, a thin, flexible tube with a small ultrasound probe at the tip is passed through your mouth or anus to reach the area of interest.
This procedure can be used to evaluate a variety of conditions, including the digestive system, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and nearby lymph nodes. The images produced by the ultrasound provide valuable information about the size, structure, and consistency of these organs and tissues.
In addition to imaging, EUS can also be used to obtain tissue samples for biopsy. This is done by using a fine needle that is passed through the endoscope to collect tissue or fluid from the area being examined. The samples obtained during an EUS can be analyzed to diagnose a variety of conditions, including cancer, infections, and inflammatory diseases.
Before undergoing an EUS, your healthcare provider will provide you with detailed instructions on how to prepare for the procedure. This typically includes guidelines on fasting and medication usage. The procedure is commonly performed on an outpatient basis, and sedation is often used to ensure your comfort throughout the process.
It’s important to discuss any concerns or questions you may have about the EUS with your healthcare provider. Understanding the purpose, process, and potential outcomes of the procedure can help you feel more informed and prepared. After the EUS, your doctor will review the findings and discuss the next steps in your care plan based on the results. If you experience any discomfort or complications following the procedure, it’s crucial to promptly inform your healthcare team.
- Preparation typically involves:
- Fasting for several hours before the procedure.
- Adjusting or temporarily stopping certain medications as directed by your doctor.
- Discussing any allergies or medical conditions with your doctor.
- During the procedure:
- You will receive sedation to help you relax.
- An endoscope with an ultrasound probe is inserted through your mouth or rectum, depending on the area being examined.
- Ultrasound images are obtained to visualize the target area.
- If necessary, FNA is performed to obtain tissue samples.
Although EUS is generally safe, potential risks include:
- Bleeding.
- Infection.
- Pancreatitis (especially after FNA of the pancreas).
- Perforation (a tear in the digestive tract).
- Reaction to the sedation.
The doctor may discuss preliminary findings immediately after the procedure. If biopsies were taken, results may take a few days.